The standard tests for measuring the Zero-Shear Viscosity are:
- Flow curve in order to determine the plateau value of the viscosity performing a shear rate controlled flow curve at low enough shear rates in steady state.
- Creep test (step stress test) in order to determine the viscosity in the stationary flow region.
- Frequency sweep in order to determine the plateau value of the complex viscosity |η*| at low enough angular frequencies.
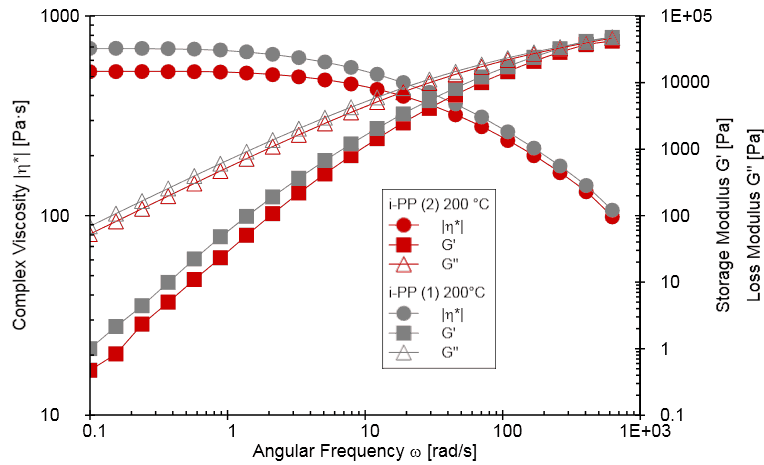
An application report produced by Anton Paar explains why the Frequency Sweep is considered the favoured method, as it provides accurate results and additional information about the molecular structure and the visco-elastic properties of a sample (storage modulus and loss modulus as well as damping factor).
In the same report, the zero-shear viscosity is calculated using the Carreau-Yasuda regression, a very practical approach for getting an average value for the relaxation time of a measured polymer sample and the Zero-Shear Viscosity, which is needed for the molar mass calculation.
Follow the link above to have your full copy of the application report with the results of this experiment.










Arriva makes £300m tri-mode train order with Hitachi Rail
This development shows up the lack of a comprehensive nationwide network of electrified lines for passenger services and freight The glacial speed of...