Showcased at Hannover Messe 2024, the 34g BionicBee is the smallest flying object created by the Bionic Learning Network to date at 220mm long and a wingspan of 240mm.
The bee’s autonomy is enabled by an indoor locating system with ultra-wideband (UWB) technology where eight UWB anchors have been installed on two levels for accurate time measurement, allowing the bees to locate themselves in the space.
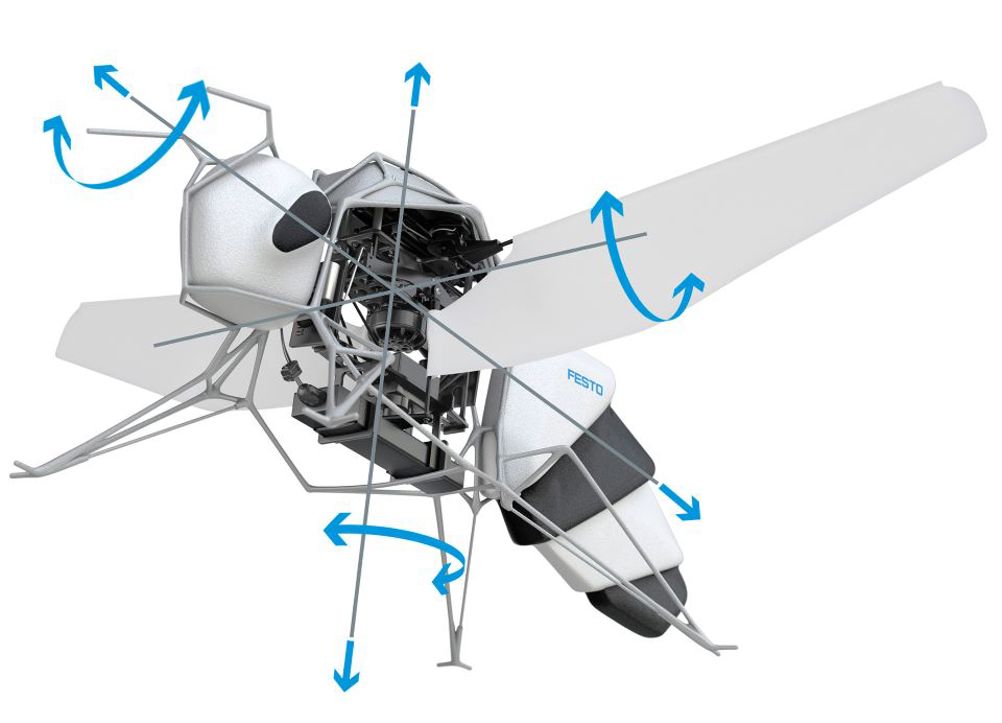
According to Festo, the UWB anchors send signals to the individual bees, which can independently measure the distances to the respective transmitting elements and calculate their own position in the space using time stamps.
To fly in a swarm, the bees follow the paths specified by a central computer. Festo added that flight planning includes ‘possible mutual interaction through air turbulence’.
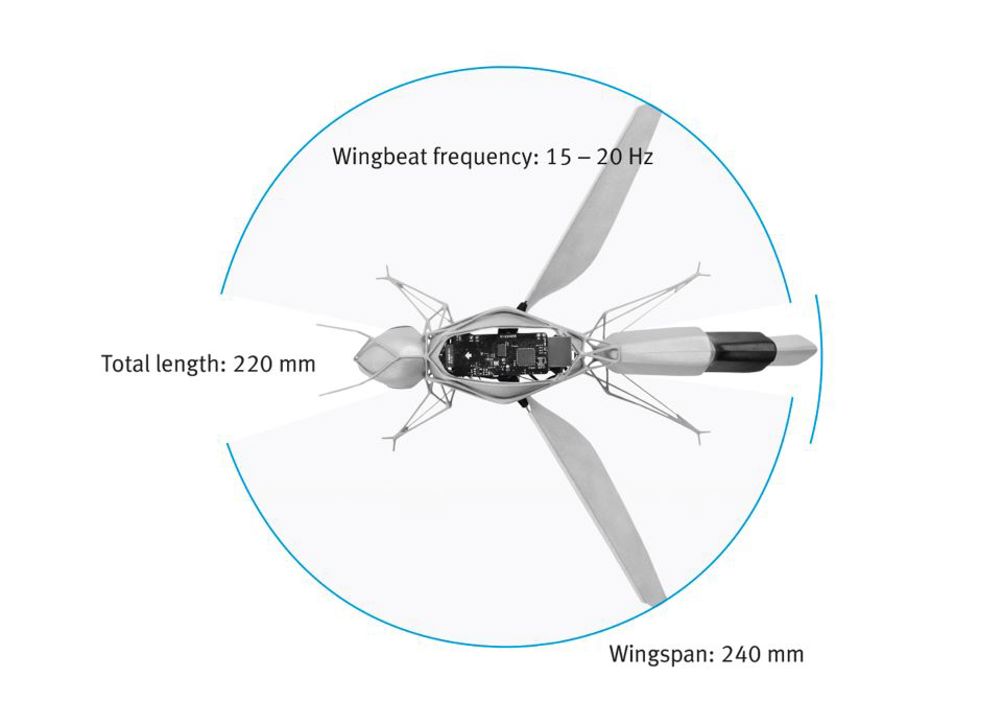
As each bee is handmade minor manufacturing differences can influence the bee’s flight behaviour, which an automatic calibration function takes into account. After a short test flight, each bee determines its individually optimised controller parameters. An algorithm calculates the hardware differences between the individual bees, allowing the swarm to be controlled from outside as if they were all identical.











IET sounds warning on AI doll trend
I agree that we need to reduce cooling water demand for servers. And yes, generative AI consumes a large amount. But what about BitCoins? Their...