Led by Martin Fussenegger from the Department of Biosystems Science and Engineering at ETH Zurich in Basel, the team has combined the fuel cell with artificial beta cells that produce insulin at the touch of a button and lower blood glucose levels. The team’s findings are detailed in Advanced Materials.
“Many people, especially in the Western industrialised nations, consume more carbohydrates than they need in everyday life,” Fussenegger said in a statement, adding that this leads to obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
“This gave us the idea of using this excess metabolic energy to produce electricity to power biomedical devices,” he said.
Central to the fuel cell is an anode made of copper-based nanoparticles that splits glucose into gluconic acid and a proton to generate electricity, setting an electric circuit in motion.
Wrapped in a nonwoven fabric and coated with alginate, the fuel cell resembles a small tea bag that can be implanted under the skin. The alginate soaks up body fluid and allows glucose to pass from the tissue into the fuel cell.
MORE FROM MEDICAL & HEALTHCARE
In a second step, the researchers coupled the fuel cell with a capsule containing artificial beta cells, which can be stimulated to produce and secrete insulin using electric current or blue LED light.
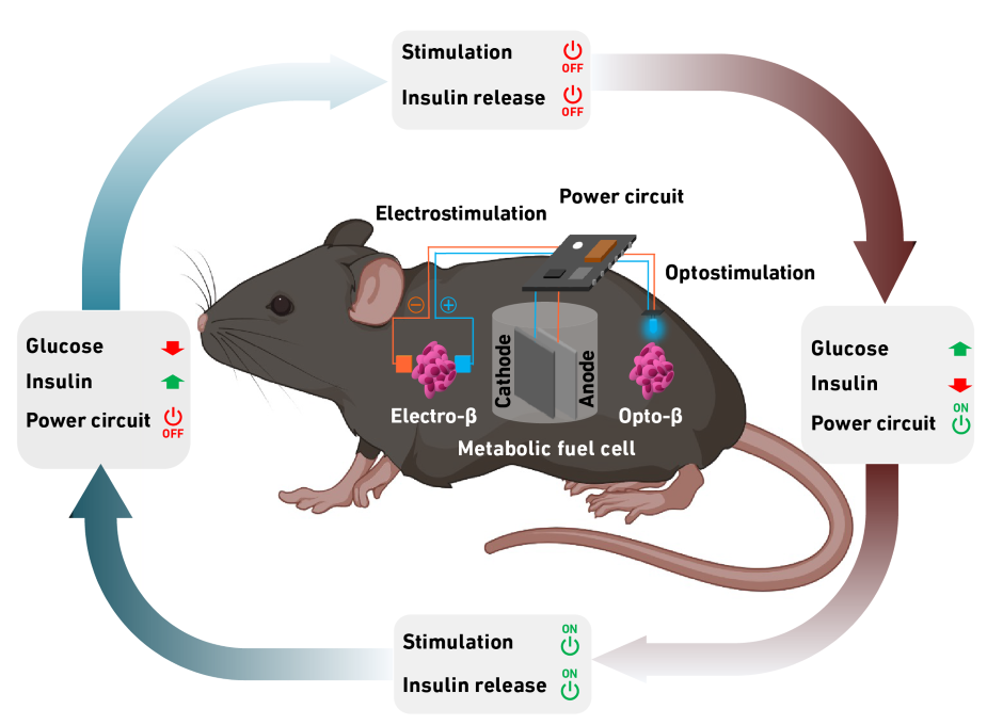
According to the team, the system combines sustained power generation and controlled insulin delivery. As soon as the fuel cell registers excess glucose, it starts to generate power. This electrical energy is then used to stimulate the cells to produce and release insulin into the blood. As a result, blood sugar dips to a normal level. Once it falls below a certain threshold value, the production of electricity and insulin stops.
The electrical energy provided by the fuel cell is sufficient not only to stimulate the designer cells but also to enable the implanted system to communicate with external devices such as a smartphone, allowing potential users to adjust the system via a corresponding app. A doctor could also access it remotely and make adjustments.
“The new system autonomously regulates insulin and blood glucose levels and could be used to treat diabetes in the future,” said Fussenegger.
The team stressed that the existing system is a prototype but has been tested successfully in mice.
“Bringing such a device to market is far beyond our financial and human resources,” said Fussenegger. “This would call for an industry partner with the appropriate resources and know-how.”











Guest blog: exploring opportunities for hydrogen combustion engines
"We wouldn't need to pillage the environment for the rare metals for batteries, magnets, or catalisers". Batteries don't use rare...